Annual Wellness Visit
If you’re covered by Medicare, you’re eligible for a fully covered comprehensive wellness exam—available in person or virtually. Prioritizing preventive care today can help you stay healthier for the long run!
Chronic care management
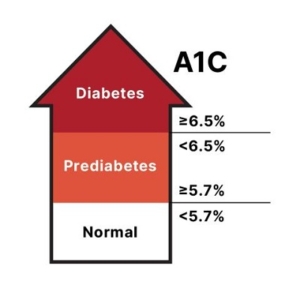
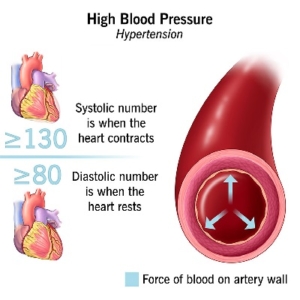
As we age, certain health conditions may require more focused care. Our team provides expert support in managing chronic conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease), and congestive heart failure, ensuring you receive the specialized attention needed to maintain your health and quality of life.
Coordination for your specialty care
When specialized care is needed, we connect you with experts who have advanced training in specific medical fields. While your specialist focuses on diagnosing and treating your condition, our team stays involved—ensuring seamless coordination and keeping your personalized care plan on track.
Optimization of Medicare Benefits
As a free service, we’ve partnered with Medicare Champion we help you navigate your insurance options. To connect with a licensed insurance agent, give us a call.
Walk out with your prescription
At many of our locations, you’ll find convenient on-site pharmacy services through Walgreens, allowing you to pick up your prescriptions the same day—right after your appointment.